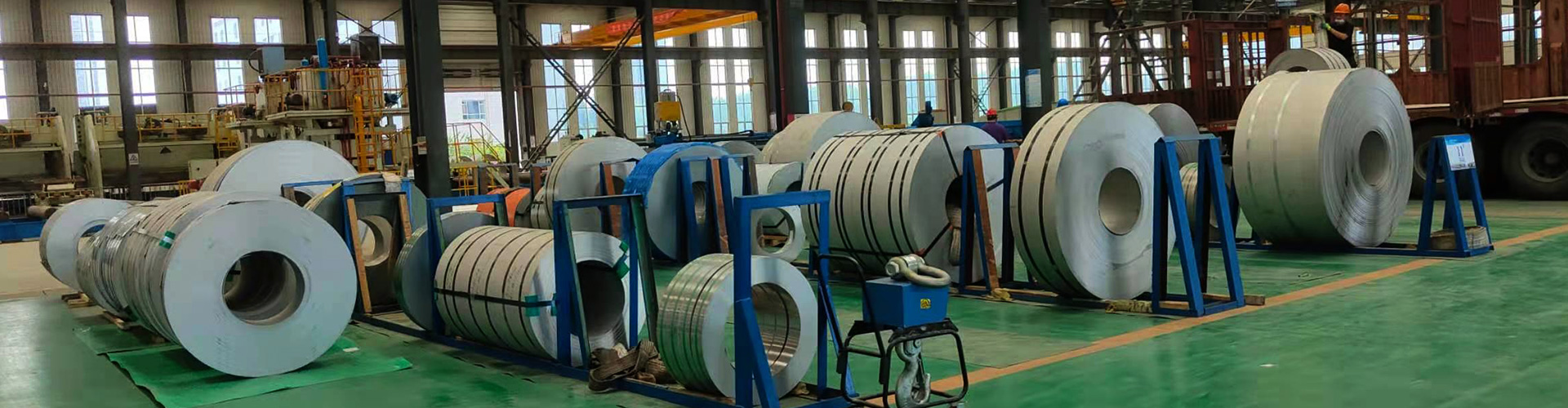

Hot rolling and cold rolling are both steel plate or profile-forming processes, which have a great impact on the structure and performance of steel. Now let us first understand what the stainless steel plate hot rolling process is.
The hot-rolled steel plate process uses slabs (mainly continuous casting billets) as raw materials, and after heating, the rough rolling mill and the finishing rolling mill produce strip steel. The hot steel strip coming out of the last rolling mill of finishing rolling is cooled to the set temperature through laminar flow and is rolled into steel strip coils by the coiler. The cooled steel strip coils undergo different finishing operations according to the different needs of users. Lines (flattening, straightening, cross-cutting or slitting, inspection, weighing, packaging and marking, etc.) are processed into steel plates, flat coils, and slit steel strip products. To put it simply, a piece of steel billet is heated and rolled several times, then trimmed and straightened into a steel plate. This is called hot rolling.
1. Poor toughness and surface smoothness, low price.
2. The temperature of hot rolling is similar to that of forging.
3. The hot plate is hot-rolled and has an oxide scale on the surface, and the thickness of the plate varies.
4. Due to its production process, it is widely used in civilian applications, such as tableware, kitchen utensils, general household appliances, etc.
5. The mechanical properties of hot-rolled steel plate are far inferior to those of cold working and inferior to forging, but it has better toughness and ductility.

It can destroy the casting structure of the steel ingot, refine the grains of the steel, and eliminate defects in the microstructure, thereby making the steel plate structure dense and improving its mechanical properties. This improvement is mainly reflected in the rolling direction so that the steel plate is no longer isotropic to a certain extent; bubbles, cracks, and looseness formed during pouring can also be welded under high temperature and pressure.
1. After hot rolling, the non-metallic inclusions (mainly sulfides, oxides, and silicates) inside the steel plate are pressed into thin sheets, resulting in delamination (sandwiching). Delamination greatly deteriorates the tensile properties of the steel plate along the thickness direction and may cause interlayer tearing when the weld shrinks. The local strain induced by weld shrinkage often reaches several times the yield point strain, which is much larger than the strain caused by the load.
2. Residual stress caused by uneven cooling. Residual stress is the internal self-balanced stress in the absence of external force. Hot-rolled steel plates of various cross-sections have such residual stress. Generally, the larger the cross-section size of the steel, the greater the residual stress. Although residual stress is self-balanced, it still has a certain impact on the performance of steel components under the action of external forces. For example, it may have adverse effects on deformation, stability, fatigue resistance, etc.
The above is about the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of stainless steel plates. If you need to purchase stainless steel plates, please pay attention to Jiangsu Tisco Tianguan Metal Products Co., Ltd. This is a Chinese stainless steel factory specializing in the production of high-quality stainless steel products.
More Knowledge About Stainless Steel
Introduction to stainless steel perforated plate manufacturing process
Characteristics and applications of TP316 and TP316L stainless steel tube
What is the difference between stainless steel 1Cr18Ni9Ti (321) and 0Cr18Ni9 (304)